What is User Interface
User Interface (UI) encompasses the visual elements, interactions, and design components of a digital product or system that users interact with. It focuses on creating an intuitive, aesthetically pleasing, and functional interface for users.
Crafting Experiences: The Essence of User Interface (UI) Design
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, User Interface (UI) Design emerges as the artistic and functional bridge between users and technology. Join us on a journey into the heart of UI design, exploring its process overview, sample use cases, and real-world case studies that showcase its transformative role in shaping engaging and intuitive digital experiences.
Process Overview: Merging Artistry with Functionality
Objective: The core objective of UI design is to create visually appealing, intuitive, and user-centric interfaces that facilitate seamless interactions between users and digital products or services.
Key Stages:
User Research
Understand the target audience, their preferences, and behaviors.
Conduct usability studies, surveys, and interviews to gather insights.
Identify user needs, pain points, and expectations.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Create wireframes to outline the basic structure and layout of the interface.
Develop interactive prototypes to visualize the user journey and interactions.
Gather feedback from stakeholders and iterate on design concepts.
Visual Design
Apply visual elements such as color schemes, typography, and imagery to enhance aesthetics.
Ensure visual consistency and alignment with brand guidelines.
Prioritize clarity and readability for optimal user comprehension.
Interaction Design
Define interactive elements and transitions to guide users through the interface.
Implement intuitive navigation and feedback mechanisms.
Ensure a seamless and delightful user experience.
User Testing
Conduct usability testing to validate design assumptions.
Gather feedback from real users on the effectiveness and usability of the interface.
Identify areas for improvement and refine the design based on user insights.
Implementation Support
Collaborate with development teams to ensure the accurate implementation of the designed interface.
Provide design specifications and assets for developers to reference.
Address any design-related challenges during the development phase.
Key Components
Responsive Design
Implement responsive design principles to ensure adaptability across various devices and screen sizes.
Prioritize a mobile-first approach to address the increasing prevalence of mobile users.
Accessibility:
Design interfaces with accessibility in mind to ensure inclusivity for users with diverse abilities.
Consider factors such as color contrast, readable fonts, and keyboard navigation.
Consistency Across Platforms
Maintain visual and interactive consistency across different platforms (web, mobile, desktop) for a unified user experience.
Use design systems and pattern libraries to streamline consistency.
Feedback Mechanisms
Integrate clear feedback mechanisms, such as hover effects, button states, and error messages.
Provide visual cues to guide users and communicate system responses.
Sample Use Cases: Elevating Experiences Through Intuitive Design
E-commerce Platform
- Objective: Enhance the user experience of an online shopping platform.
- UI Design Focus: Streamline the product catalog layout, optimize the checkout process, and improve navigation.
- Outcome: Users benefit from an intuitive and visually appealing shopping experience, leading to increased conversions and customer satisfaction.
Fitness App
- Objective: Develop a user-friendly fitness app with a focus on tracking and personalization.
- UI Design Focus: Create a visually engaging dashboard, design intuitive workout tracking interfaces, and implement personalized user profiles.
- Outcome: The app becomes a go-to tool for fitness enthusiasts, offering an aesthetically pleasing and motivating experience.
Corporate Intranet
- Objective: Redesign a corporate intranet for improved employee engagement and productivity.
- UI Design Focus: Optimize information architecture, implement a clean and organized dashboard, and enhance collaboration features.
- Outcome: Employees experience a more visually appealing and user-friendly intranet, fostering increased engagement and streamlined workflows.
News Aggregator
- Objective: Develop a news aggregator app for diverse content consumption.
- UI Design Focus: Create an intuitive content discovery interface, implement clear navigation, and prioritize readability.
- Outcome: Users find the app visually appealing and easy to navigate, leading to increased user retention and content consumption.
Case Studies: UI Design in Action
Apple iOS:
- Challenge: Apple aimed to revolutionize mobile user interfaces with the introduction of the iPhone.
- UI Design Implementation: Introduced a touch-based interface, minimalist design principles, and a cohesive design language.
- Outcome: The iPhone’s UI design set industry standards, offering users a visually appealing and intuitive mobile experience.
Google Material Design:
- Challenge: Google sought to establish a consistent design language across its various platforms.
- UI Design Implementation: Introduced Material Design, a design system emphasizing visual consistency, motion, and responsiveness.
- Outcome: Google’s platforms, including Android apps and web services, adopted a unified and aesthetically pleasing UI design, enhancing user familiarity and satisfaction.
Airbnb Redesign:
- Challenge: Airbnb aimed to improve the booking experience and increase user engagement.
- UI Design Implementation: Revamped the interface with a focus on larger visuals, simplified navigation, and improved content organization.
- Outcome: The redesigned interface led to a significant increase in user engagement and bookings, showcasing the impact of UI design on user behavior.
Navigating Challenges: Maximizing the Impact of UI Design
To ensure the optimal impact of UI design, organizations should address common challenges:
User Feedback Integration
Actively incorporate user feedback into the UI design process to address usability issues and align with user preferences.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Foster collaboration between UI designers, developers, and other stakeholders to ensure seamless implementation and adherence to design principles.
Evolution with Technology
Stay abreast of technological advancements and evolving user behaviors to adapt UI designs to emerging trends.
Usability Testing
Regularly conduct usability testing with real users to identify pain points and gather insights for iterative improvements.
The Art and Impact of UI Design
User Interface Design is more than just a visual aesthetic—it’s a dynamic blend of artistry and functionality that shapes the digital experiences of millions. Through a comprehensive process overview, sample use cases, and real-world case studies, we’ve unveiled the transformative power of UI design—from revolutionizing mobile interfaces with Apple iOS to fostering a cohesive design language with Google Material Design.
As technology continues to advance, UI design remains at the forefront of creating meaningful connections between users and digital products. It’s a testament to the commitment to user-centricity, where every pixel, color choice, and interaction is carefully crafted to deliver an immersive and delightful experience. In the journey of crafting digital landscapes, UI design stands as the compass that guides users through seamless, engaging, and aesthetically pleasing journeys.
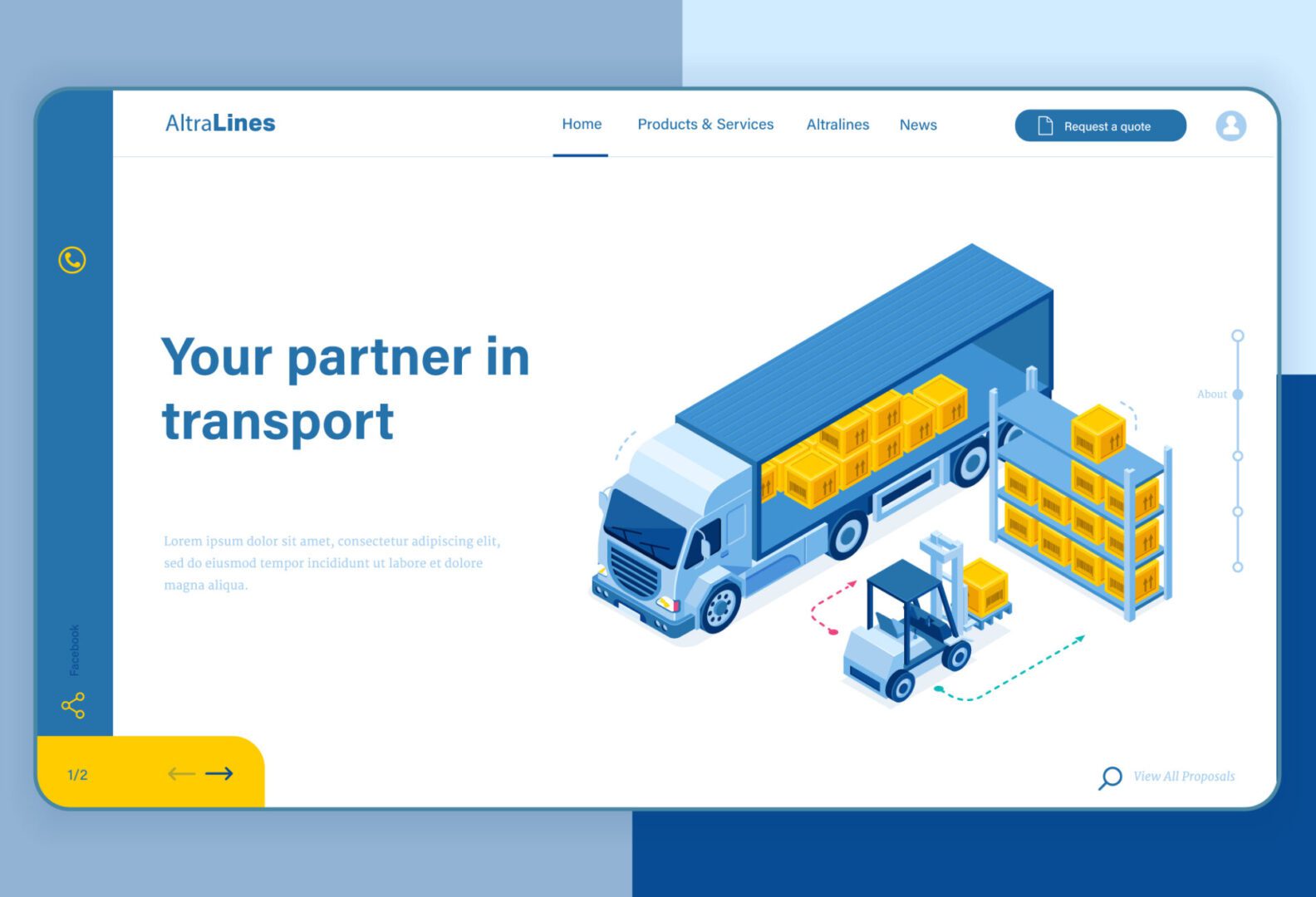
Importance
Visual Design: Aesthetics, colors, typography, and layout of elements.
Interactive Elements: Buttons, forms, navigation, and other functional components.
Usability: Designing for ease of use, accessibility, and user satisfaction.
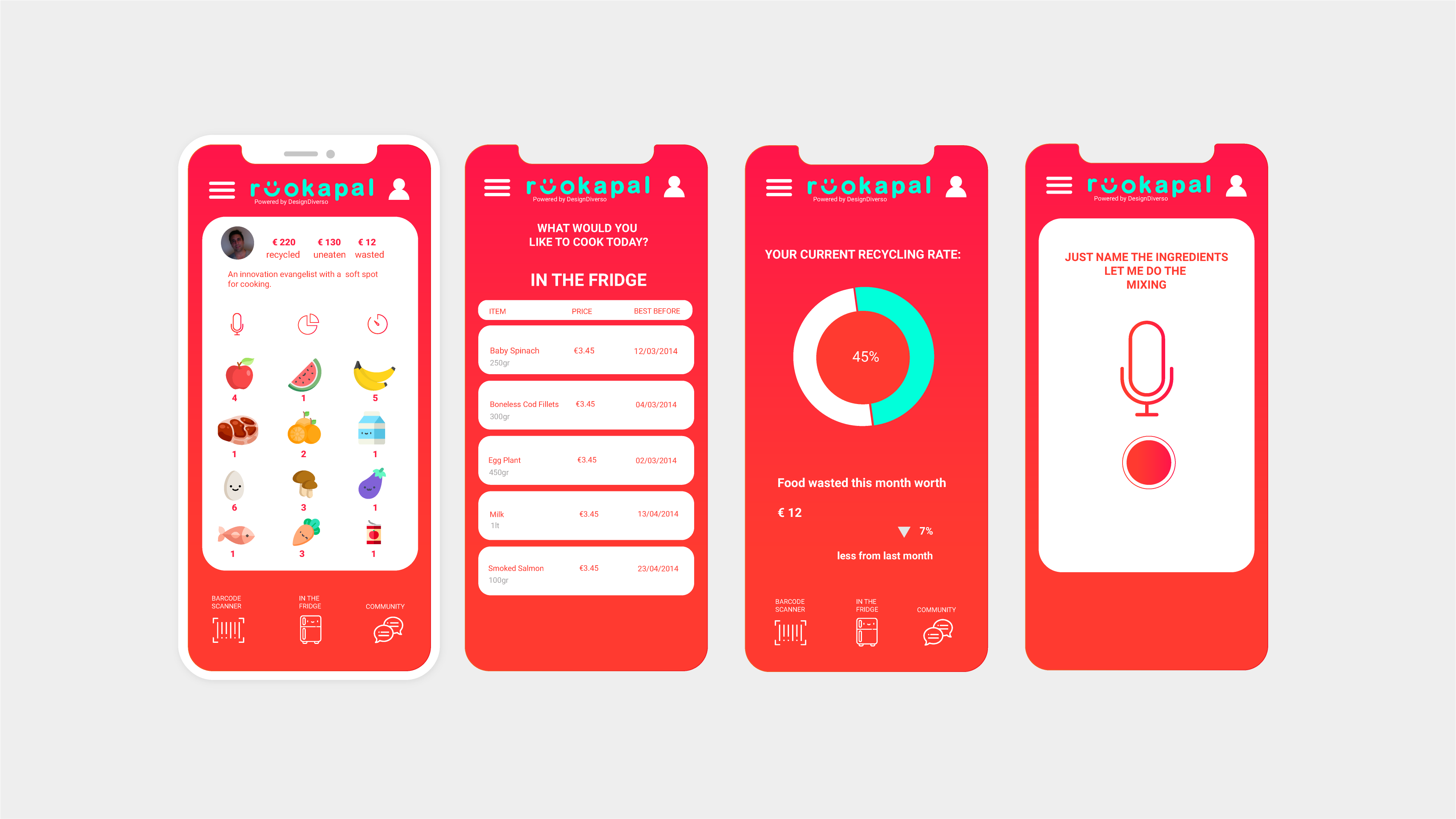
Your Business Benefits
Enhanced User Experience: Intuitive UI leads to better user satisfaction.
Improved Engagement: Engaging and user-friendly interfaces encourage interaction.
Brand Consistency: UI design reinforces brand identity and recognition.
Your Business Strategies
User-Centered Design: Prioritize user needs and behaviors in UI design.
Consistent Design Language: Maintain consistency in UI elements and interactions.
Accessibility Considerations: Ensure UI is accessible to diverse user groups.

