What are Personas
Personas are fictional characters representing different user types or segments that interact with a product or service. They are based on real data and research and help in understanding user needs, behaviors, and goals.
The Human Touch in Design
In the ever-evolving landscape of user-centric design, personas emerge as the empathetic architects, giving a face and a story to the diverse audience that interacts with products and services. Beyond demographic data, personas encapsulate the motivations, behaviors, and goals of users, guiding designers, marketers, and product teams toward creating experiences that resonate. Join us as we explore the world of personas, uncovering their strategic significance, sample use cases, and real-world case studies that illuminate their transformative role in understanding and catering to the needs of diverse user groups.
The Empathetic Cornerstone of User-Centric Design
What are Personas? Personas are detailed and fictional representations of idealized users, created to embody the characteristics and behaviors of different segments of a target audience. They serve as archetypal user profiles that encapsulate key attributes, goals, challenges, and preferences, providing a human-centric lens through which teams can understand and address user needs.
The Significance of Personas
User Empathy: Personas foster empathy by humanizing users. Designers and teams can better relate to the diverse motivations and challenges of their audience, leading to more thoughtful and user-centric solutions.
Targeted Communication: Personas guide communication strategies by helping teams understand the preferred channels, messaging, and content that resonate with specific user segments. This targeted approach enhances engagement and connection.
Informed Decision-Making: Personas inform decision-making across various stages of product development. From design choices to feature prioritization, personas provide a user-focused framework for making informed and strategic decisions.
Alignment Across Teams: Personas create a shared understanding of the target audience across multidisciplinary teams. Marketing, design, development, and other stakeholders can align their efforts to ensure a cohesive and user-centric approach.
Tailoring Experiences to Diverse Audiences – Sample use cases
E-commerce Platform:
- Objective: Enhancing the user experience of an e-commerce website.
- Personas Created:
- Savvy Shopper Sarah: Frequent online shopper looking for deals and promotions.
- Time-Pressed Tom: Busy professional seeking quick and efficient shopping experiences.
- Outcome: Tailored user interfaces, personalized recommendations, and targeted promotional strategies for each persona, resulting in improved user satisfaction and increased conversion rates.
Health and Fitness App:
- Objective: Designing a fitness app that caters to various user needs.
- Personas Created:
- Fitness Enthusiast Emily: Enjoys detailed workout plans and tracking progress.
- Beginner Ben: Looking for easy-to-follow routines and motivational content.
- Outcome: Customized workout plans, personalized progress tracking features, and targeted content based on the preferences and goals of each persona, leading to higher user engagement.
Financial Planning Tool:
- Objective: Developing a financial planning tool for a diverse user base.
- Personas Created:
- Investor Ian: Interested in detailed investment insights and portfolio management.
- Budgeting Betty: Focused on tracking expenses, creating budgets, and saving money.
- Outcome: Tailored dashboards, personalized financial advice, and targeted educational resources for each persona, resulting in increased user satisfaction and retention.
Travel Booking Website:
- Objective: Improving the user experience of a travel booking platform.
- Personas Created:
- Adventurous Alex: Seeks unique and off-the-beaten-path travel experiences.
- Family-Focused Fiona: Values family-friendly accommodations and travel options.
- Outcome: Personalized travel recommendations, targeted promotions, and user interfaces designed to meet the specific needs and preferences of each persona, leading to increased bookings and positive user feedback.
Case Studies: Personas in Action
Microsoft Office 365:
- Challenge: Microsoft aimed to enhance the user experience of its Office 365 suite.
- Personas Created:
- Productivity Pro Paul: A power user seeking advanced features for efficient work.
- Casual User Clara: Prefers a simplified interface for basic tasks.
- Result: Microsoft implemented interface customizations, feature suggestions, and user guides tailored to the distinct needs of each persona, resulting in improved user satisfaction and adoption.
HubSpot Marketing Software:
- Challenge: HubSpot sought to optimize its marketing software for a diverse user base.
- Personas Created:
- Marketing Maven Mia: Seeks advanced analytics and automation features.
- Startup Steve: Requires user-friendly tools for a streamlined marketing approach.
- Result: HubSpot incorporated persona-driven feature sets, user onboarding paths, and targeted educational content, resulting in increased user engagement and positive feedback.
Facebook:
- Challenge: Facebook aimed to enhance its ad targeting capabilities.
- Personas Created:
- Social Media Marketer Sam: Interested in precise audience targeting for marketing campaigns.
- Small Business Owner Olivia: Seeks affordable and effective ad solutions for her business.
- Result: Facebook utilized persona-driven insights to refine its ad targeting options, ensuring that marketers and small businesses could reach their intended audiences more effectively.
Navigating Challenges: Maximizing the Impact of Personas
While personas offer valuable insights, addressing challenges ensures their optimal impact:
Data-Driven Accuracy: Ensure that persona development is based on accurate and comprehensive user data. Regularly update personas to reflect evolving user behaviors and preferences.
Balancing Specificity: While personas should be detailed, striking the right balance is crucial. Avoid over-specifying characteristics to maintain broad applicability and relevance across diverse user groups.
Inclusive Representation: Ensure that personas represent the diversity of the target audience. Consider factors such as demographics, psychographics, and cultural backgrounds to create inclusive and representative personas.
Continuous Validation: Regularly validate personas through user research, testing, and feedback. As user behaviors and preferences evolve, ongoing validation ensures that personas remain accurate and relevant.
Human-Centered Design for Lasting Impact
In the intricate tapestry of user-centric design, personas stand as the vivid threads weaving together user needs, aspirations, and behaviors. Through sample use cases and case studies, we’ve witnessed the transformative impact of personas—from shaping the design of financial planning tools to optimizing marketing software.
As organizations navigate the complexities of user interactions, personas serve as invaluable guides, fostering empathy, aligning teams, and shaping experiences that resonate on a human level. In the symphony of human-centered design, personas are the conductors, orchestrating a harmonious blend of user-centric strategies that lead to lasting impact, memorable user experiences, and products that truly understand and cater to the diverse needs of their audience.

Importance
User Segmentation: Identifies and categorizes users based on traits.
Behavioral Insights: Represents goals, motivations, and pain points.
Empathy Building: Helps in empathizing with different user groups.
User-Centric Design: Guides design decisions based on user needs.
Empathy and Understanding: Helps in understanding diverse user perspectives.
Product Validation: Validates features against user preferences and behaviors.
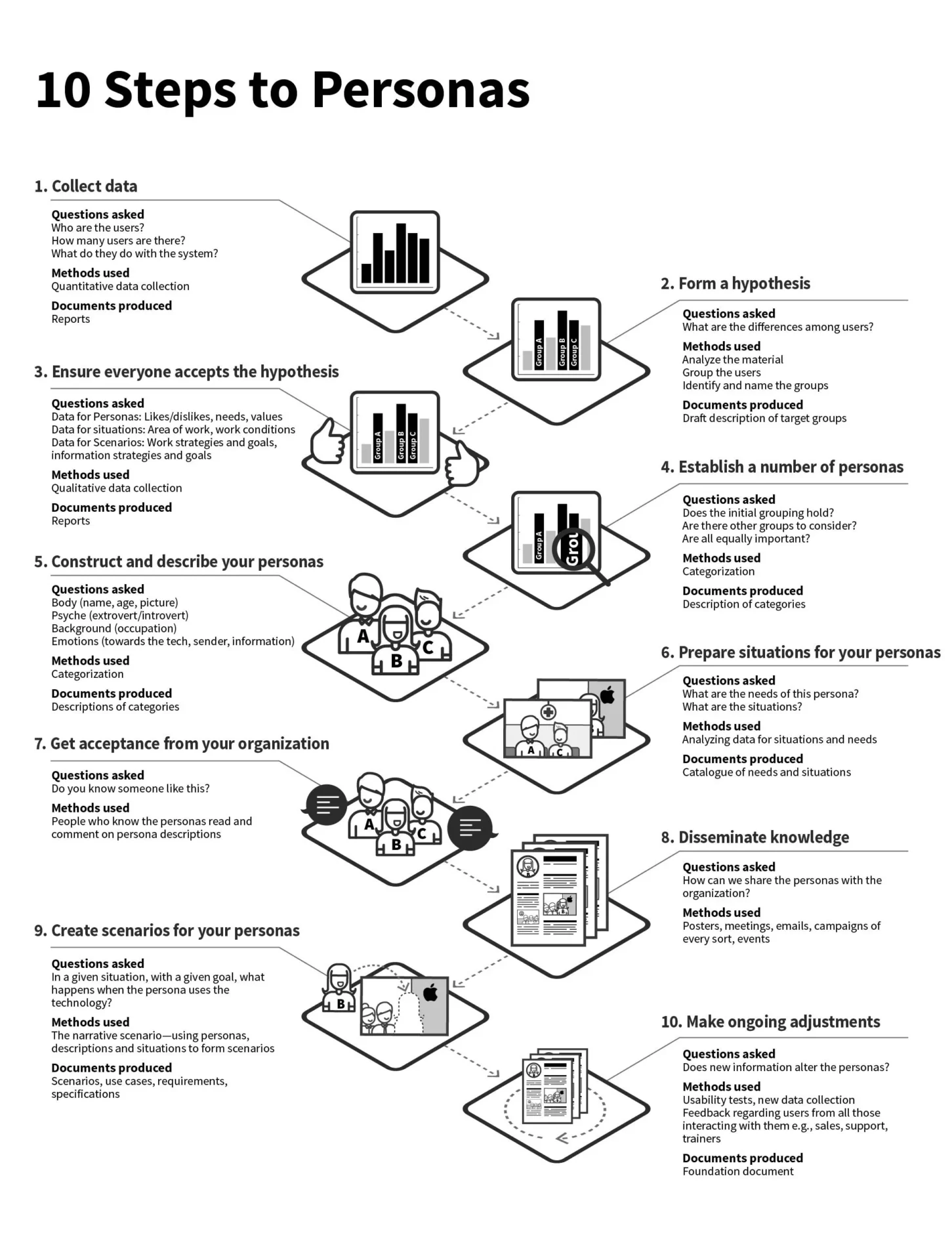
Process Overview
Objective
The goal of the personas development process is to create detailed and representative fictional characters that embody the key characteristics, needs, and behaviors of different user segments. These personas serve as invaluable tools for guiding user-centric design decisions and ensuring a human-centered approach to product development.
Key Stages
Initiation:
Identifying the need for personas based on project goals and user-centric design principles.
Defining the scope of the personas development process, including target audience and key user segments.
Assembling a cross-functional team including designers, marketers, and product managers.
Research and Data Collection:
Conducting thorough user research to gather demographic, psychographic, and behavioral data.
Utilizing a variety of methods such as surveys, interviews, and analytics to collect insights.
Identifying common patterns and trends within the target audience.
Persona Creation:
Developing detailed and realistic personas based on the collected data.
Including information such as age, gender, job role, goals, pain points, and motivations.
Creating distinct personas representing different user segments within the target audience.
Validation:
Sharing the developed personas with stakeholders and team members for feedback.
Validating personas through additional user testing and research to ensure accuracy.
Refining and adjust personas based on feedback and validation results.
Documenting each persona, providing a comprehensive overview of their characteristics.
Including visual representations, names, and detailed narratives for better engagement.
Ensuring documentation is easily accessible to all team members involved in the design and development process.
Key Components
Roles and Responsibilities:
Clearly define the roles responsible for gathering data, creating personas, and validating the accuracy of the personas.
Establish a collaborative environment that encourages input from cross-functional teams.
Communication Plan:
Implement a communication plan to facilitate collaboration among team members.
Regularly update stakeholders on the progress of the personas development process.
Validation and Testing Plan:
Develop a plan for user testing and validation to ensure personas accurately represent the target audience.
Identify key metrics and criteria for successful validation.
Documentation Guidelines:
Establish guidelines for creating detailed and informative persona documents.
Ensure consistency in the format and content of personas to enhance usability.
Interconnected Processes:
The personas development process is closely linked to user research, design, and marketing strategies. It informs decisions in product development, content creation, and user experience design.
Key Success Factors
Comprehensive Research: Thorough user research lays the foundation for accurate and effective personas.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Successful personas development requires collaboration among designers, marketers, and other relevant stakeholders.
Continuous Iteration: Regularly update personas based on changing user behaviors and project requirements.
Validation and Feedback: Actively seek validation and feedback from stakeholders to ensure the accuracy and relevance of personas.
Your Business Benefits
Targeted Design: Designs catered to specific user needs and behaviors.
Reduced Assumptions: Provides factual insights into user behaviors.
Improved UX: Enhances user satisfaction by addressing user needs.
Your Business Strategies
Research and Data: Base personas on extensive user research and data.
User Interviews: Gather insights from real users to create accurate personas.
Regular Updates: Update personas based on evolving user behavior and needs.

