What is HIgh Fidelity
A high-fidelity prototype refers to a detailed and close-to-final representation of a digital product or interface, often created using advanced design tools or coding. It closely resembles the final product in terms of functionality and appearance.
The Art and Impact of High-Fidelity Prototypes
In the dynamic landscape of product development, where ideas are the seeds of innovation, High-Fidelity Prototypes emerge as the canvas where concepts transform into tangible, interactive experiences. Far beyond simple mock-ups, these prototypes embody the essence of precision and detail, serving as the bridge between imagination and reality. Let’s delve into the world of High-Fidelity Prototypes, exploring their significance, sample use cases, and real-world case studies that showcase their transformative influence on the innovation journey.
Understanding High-Fidelity Prototypes: Precision in Progress
What are High-Fidelity Prototypes? High-Fidelity Prototypes are advanced, detailed representations of a product or system, providing a realistic simulation of the final user interface or experience. Unlike low-fidelity counterparts, these prototypes encapsulate intricate design elements, interactions, and functionalities, offering stakeholders a vivid preview of the end product’s look and feel.
The Significance of High-Fidelity Prototypes:
Visual Realism
High-Fidelity Prototypes capture the visual essence of the final product, including colors, typography, and layout. This realism helps stakeholders visualize the end result and make informed decisions.
User Interaction Simulation
Through interactive elements, High-Fidelity Prototypes replicate the actual user experience. This includes clickable buttons, responsive interfaces, and dynamic transitions, providing a comprehensive understanding of how users will engage with the final product.
Validation of Design Concepts
By presenting a lifelike version of the design, High-Fidelity Prototypes facilitate the validation of design choices. Stakeholders can assess aesthetics, usability, and overall user satisfaction in a manner not possible with lower-fidelity alternatives.
Reduced Misinterpretation
The precision and detail in High-Fidelity Prototypes leave little room for misinterpretation. They serve as a common ground for designers, developers, and stakeholders, aligning expectations and minimizing misunderstandings.
Sample Use Cases: High-Fidelity Prototypes in Action
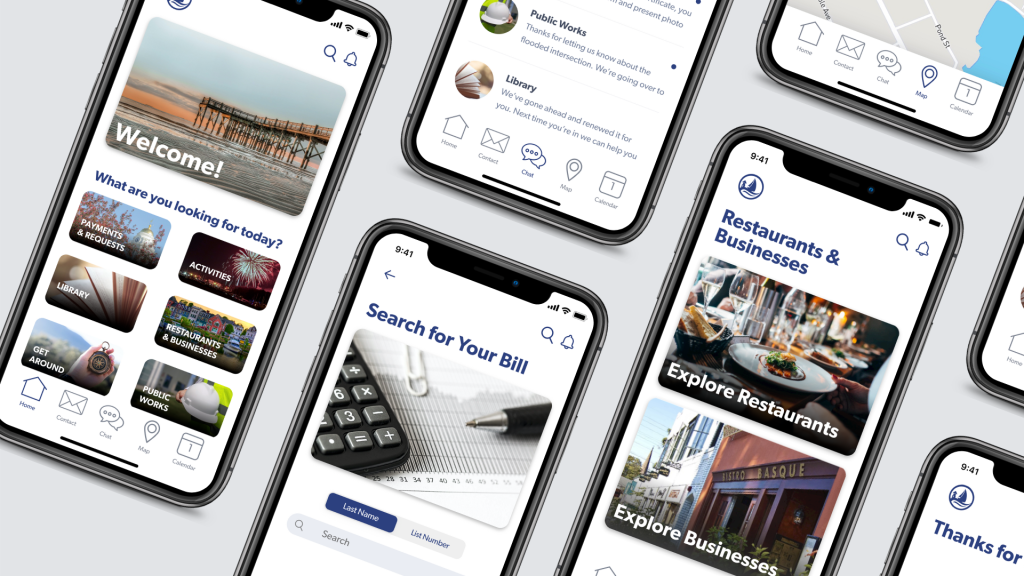
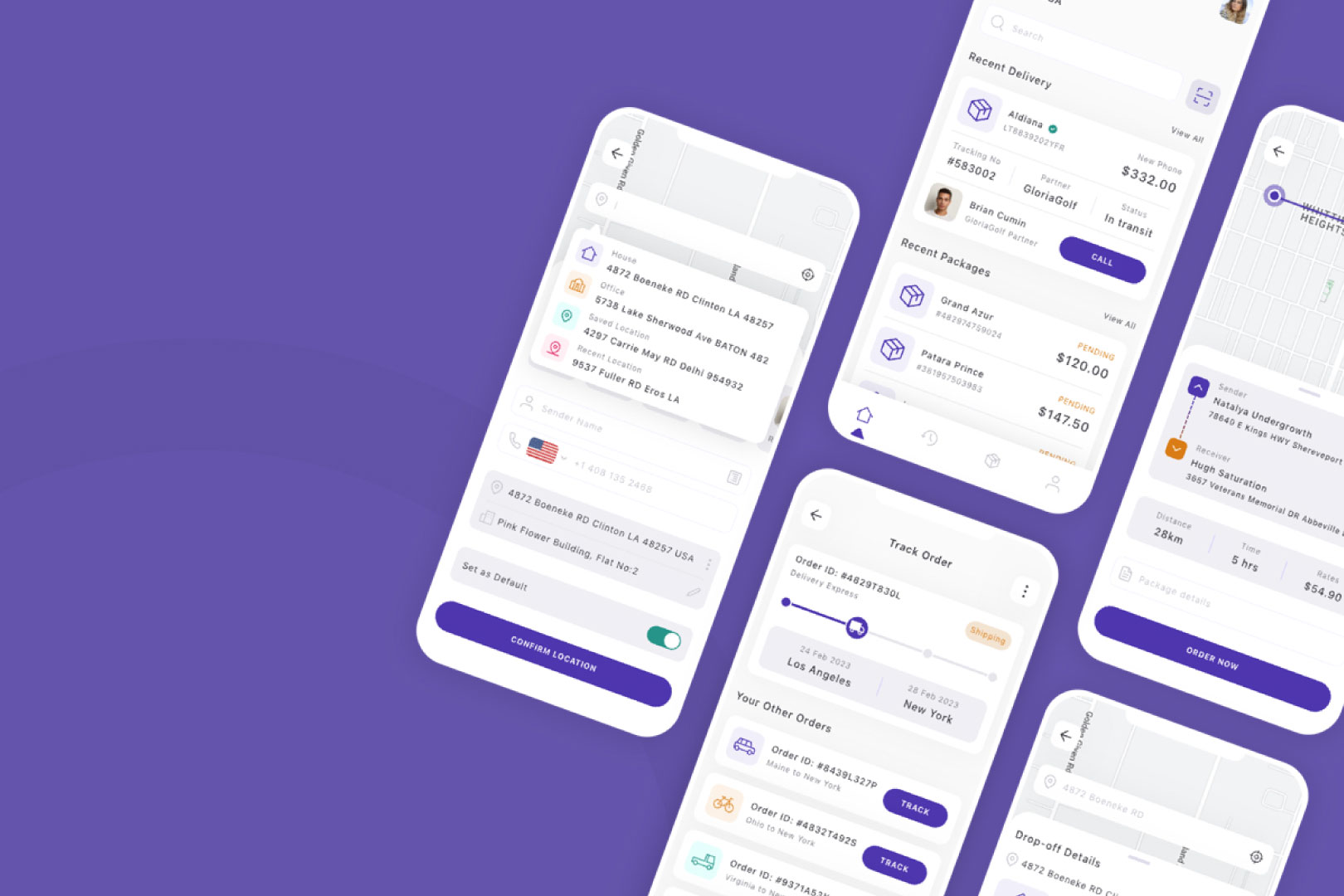
Mobile App Development:
- Objective: Designing an intuitive and visually appealing mobile application.
- Process: High-Fidelity Prototypes showcase the app’s interface, navigation, and interactive features. Stakeholders can experience the flow of screens, test navigation paths, and provide feedback on the visual elements.
- Outcome: The final app benefits from user-centric design choices, streamlined navigation, and a visually cohesive interface, leading to improved user satisfaction.
Website Redesign:
- Objective: Revamping an existing website to enhance user engagement.
- Process: High-Fidelity Prototypes demonstrate the redesigned website’s layout, color scheme, and interactive elements. Stakeholders can navigate through pages, explore new features, and assess the overall user experience.
- Outcome: The redesigned website aligns with stakeholder expectations, incorporates user-friendly enhancements, and achieves a modern, cohesive look.
E-Learning Platform:
- Objective: Developing an engaging and effective e-learning platform.
- Process: High-Fidelity Prototypes simulate the platform’s user interface, interactive modules, and assessment features. Stakeholders can interact with sample lessons, test navigation, and provide feedback on the instructional design.
- Outcome: The final e-learning platform benefits from a user-friendly interface, seamless navigation, and optimized content delivery, resulting in enhanced user engagement and learning outcomes.
Product Packaging Design:
- Objective: Creating visually appealing and market-ready product packaging.
- Process: High-Fidelity Prototypes visualize the packaging design in 3D, considering colors, textures, and placement of branding elements. Stakeholders can assess the shelf appeal, tactile qualities, and overall visual impact.
- Outcome: The final product packaging stands out on shelves, communicates brand identity effectively, and aligns with market expectations.
Case Studies: High-Fidelity Prototypes in Practice
Airbnb’s Redesign Exploration:
- Challenge: Airbnb aimed to enhance the user experience and revamp its platform.
- Solution: The design team created High-Fidelity Prototypes to showcase potential redesign concepts, incorporating new features and improved navigation. Stakeholders interacted with the prototypes to provide feedback.
- Result: The redesign, informed by the insights gained from High-Fidelity Prototypes, led to a more intuitive platform, increased user engagement, and positive feedback from both hosts and guests.
Tesla’s In-Car User Interface Upgrade:
- Challenge: Tesla sought to upgrade the in-car user interface for its electric vehicles.
- Solution: High-Fidelity Prototypes were utilized to simulate the new user interface, including touch screen interactions, visualization of vehicle data, and integration of new features. Stakeholders, including drivers, provided feedback during the testing phase.
- Result: The upgraded in-car user interface, informed by High-Fidelity Prototypes, delivered a seamless and visually appealing experience, enhancing driver satisfaction and setting new standards in automotive technology.
Google’s Material Design Language:
- Challenge: Google aimed to create a cohesive design language across its various platforms and devices.
- Solution: High-Fidelity Prototypes were employed to showcase the visual and interactive aspects of the Material Design language. Designers, developers, and stakeholders collaborated using the prototypes to ensure consistency and alignment.
- Result: The Material Design language, shaped by High-Fidelity Prototypes, became a standard for Google’s user interfaces, providing a unified and visually pleasing experience across a diverse range of products.
Maximizing High-Fidelity Impact
While High-Fidelity Prototypes offer a myriad of benefits, navigating challenges ensures their optimal impact:
Resource Intensity
High-Fidelity Prototypes can be resource-intensive in terms of time and effort. It’s crucial to balance the level of detail with project timelines and available resources.
Feedback Incorporation
Gathering and incorporating feedback from stakeholders during the prototype phase is essential. Establishing a feedback loop ensures that the final product aligns with expectations and user needs.
Cost Considerations
Developing High-Fidelity Prototypes can incur costs, especially in complex projects. Prioritizing features and focusing on critical aspects can help manage costs while still delivering a realistic representation.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective collaboration between design, development, and stakeholder teams is vital. Ensuring a shared understanding and alignment of objectives helps in maximizing the impact of High-Fidelity Prototypes.
Precision in Progress, Excellence in Execution
In the realm of product development, where precision meets innovation, High-Fidelity Prototypes stand as the epitome of progress. Through sample use cases and case studies, we’ve witnessed the transformative impact of these prototypes—from shaping digital interfaces to influencing product packaging and user experiences.
As organizations embark on the journey of bringing ideas to life, High-Fidelity Prototypes emerge as indispensable tools, offering a tangible preview of the envisioned future. They are the compass guiding designers, developers, and stakeholders toward a shared destination of excellence. In the symphony of innovation, High-Fidelity Prototypes play a harmonious tune, orchestrating the seamless transition from imagination to reality.
Process Overview
Detailed Design
Represents the actual design elements and functionalities.
Interactivity
Allows for user interactions and simulations of the final product.
Visual Realism
Mimics the appearance and aesthetics of the final product.
Importance
Comprehensive Testing
Enables thorough testing of functionalities and interactions.
User Feedback
Facilitates gathering feedback and validation from stakeholders or users.
Reduced Development Risks
Helps in identifying issues early, reducing development risks.
Your Business Benefits
Validation and Testing
Allows for comprehensive testing and validation of features.
Stakeholder Communication
Communicates the final product vision effectively to stakeholders.
Reduced Development Costs
Identifies and addresses issues early in the process.
Your Business Strategies
Iterative Prototyping
Iteratively refine high-fidelity prototypes based on feedback.
User Testing
Gather user feedback and iterate based on user interactions.
Collaborative Feedback
Involve stakeholders for comprehensive input and validation.

